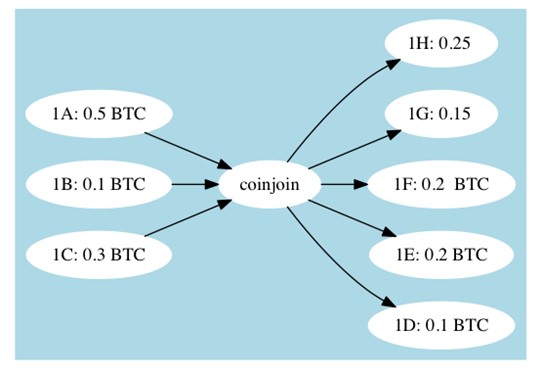
Every Bitcoin transaction's history can be traced, and on-chain data analysis companies can identify fund flows and associate different addresses
Repeatedly receiving funds to a single address exposes your financial status; anyone who knows your address can view your balance and transaction history
Businesses using Bitcoin may inadvertently disclose sensitive supply chain and customer information to competitors
Publicly visible large balances can make you a target for hacker attacks or real-world threats